Peek Into the World of Sun Protection with SPF 30 VS SPF 50

We know bronze can be beautiful, but with all of the amazing options for faux, the real deal is off the table - especially with what we know now about the damages the sun can inflict on the skin. Read on to learn more about SPF 30 vs SPF 50. This will help you learn how to protect your skin from sun damage, including wrinkles, premature aging, lines, sagging, and cancer; if you love the sun-kissed look, turn to cosmetics to recreate the glow it gives you, and keep your gorgeous skin fresh and beautiful for your lifetime! Read on to learn the difference between SPF 30 and 50 in our well-structured blog.
What is SPF?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor and is a measure of how well a sunscreen can protect the skin from UVB rays, which are primarily responsible for sunburns. SPF does not directly indicate protection against UVA rays, which are associated with long-term skin damage and premature aging. Using a sunscreen is as important as drinking water to stay hydrated! Your skin needs a sunscreen of SPF 30 or 50 depending on different factors.
What is the difference between UVA and UVB rays?

UVB rays primarily affect the skin's outermost layer and are the main cause of sunburns. On the other hand, UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, contributing to premature aging, wrinkles, and skin cancer. Both UVA and UVB rays are harmful, emphasizing the need for broad-spectrum sunscreens that protect against both types of radiation.
So…how does sunscreen work exactly?
Sunscreen is a crucial component of skincare, protecting our skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. It works by forming a protective barrier on the skin's surface, shielding it from the damaging effects of the sun. To understand how sunscreen accomplishes this, we need to examine its active ingredients and emulsion.
What are the active ingredients in sunscreen, SPF 30 Vs SPF 50?

The active ingredient in sunscreen plays a vital role in its sun protection capabilities. Common active ingredients include organic compounds like oxybenzone, avobenzone, and octinoxate, as well as mineral compounds such as zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
These ingredients work by absorbing or reflecting UV radiation, preventing it from penetrating the skin. This prevents the skin from burning, which is a huge factor in preventing skin cancers like melanoma.
Organic compounds, also known as chemical sunscreens, absorb UV rays and convert them into less harmful forms of energy, such as heat. On the other hand, mineral compounds, referred to as physical or mineral sunscreens, create a physical barrier on the skin's surface, reflecting and scattering UV radiation away from the skin.
Both are good ways to prevent the sun from damaging your skin, something that seems unimportant in your youth but that you will appreciate more and more as you age. Combined, physical and chemical barriers can provide a strong defense against sun damage.
What is emulsion, and why does it matter?
The emulsion in sunscreen refers to the formulation that helps deliver the active ingredients evenly onto the skin; in short, it’s the delivery system of your sunscreen. Sunscreens are typically formulated as either creams, lotions, gels, or sprays. These emulsions ensure that the active ingredients are spread uniformly, allowing for optimal sun protection. While sprays are certainly widely available on the market, they’re not our preferred form of delivery, especially for children or people with respiratory problems, as they can exacerbate allergic reactions and make it harder to breathe.
BelleCôte's Double Sun Protection Cream is an example of a sunscreen that combines the efficacy of both chemical and physical sunscreens. The delivery system, or emulsion, it uses, is a rich cream that spreads easily and evenly over the skin, without a greasy feeling or lingering film on the skin. Its advanced formulation ensures effective sun protection while providing a comfortable texture for easy application.
How should I apply sunscreen?

When applying sunscreen, it is essential to follow the recommended guidelines for adequate protection. Experts suggest applying a generous amount of sunscreen to all exposed areas of the skin, around 15 to 30 minutes before sun exposure. This allows time for the sunscreen to bind to the skin and provide optimal protection. It’s always a good idea to double check that you’ve gotten easy-to-miss areas of the skin, like the ears, tops of the feet, bock of the shoulders and neck, the chest and decolletage, hands, and any other spot that you know you’re prone to forgetting or burning in the past.
How long can I expect my SPF to last?
The effectiveness of sunscreen varies depending on factors such as the SPF level, sweat, water exposure, and the intensity of UV radiation. Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours, or more frequently if sweating or swimming. Even water-resistant sunscreens can lose their efficacy over time, so it is crucial to reapply regularly. In addition, make sure you check the expiration date on your sunscreen. Expired sunscreen cannot be trusted to work! Don’t risk your skin - throw it away and use new product.
SPF 30 VS SPF 50: A Comparison
You’ve probably held each bottle or spray in your hand, pondering the real differences between the two, and wondering which is the right choice for you. Ponder no longer!
SPF 30
SPF 30 indicates that the sunscreen provides 30 times the protection against UVB rays compared to unprotected skin. For example, if it takes 10 minutes for your skin to start turning red in the sun without sunscreen, applying SPF 30 would theoretically allow you to stay in the sun for 300 minutes (10 minutes multiplied by SPF 30).
SPF 50
SPF 50 offers 50 times the protection against UVB rays compared to unprotected skin. Using the same example as before, if it takes 10 minutes for your skin to start reddening without sunscreen, SPF 50 would theoretically provide protection for up to 500 minutes (10 minutes multiplied by SPF 50).
So which should I choose...SPF 30 or 50?

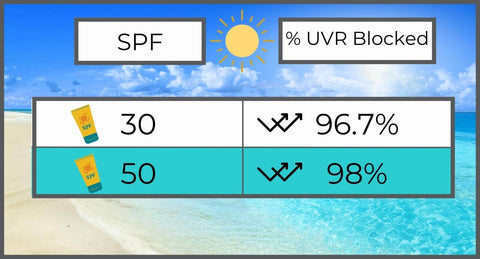
While there is a numerical difference between SPF 30 and SPF 50, it is important to note that the additional protection provided by SPF 50 is not significantly higher. SPF 30 filters around 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 filters approximately 98%. The difference is minimal, but it can be beneficial for those with extremely fair or sensitive skin. If you have a history of skin cancer in your family, or you burn very easily, use SPF 50. Otherwise, SPF 30 should be sufficient. Anything over SPF 50 isn’t really necessary, but won’t hurt or lack efficacy.
BelleCôte's Skincare Regimen

BelleCôte's skincare regimen emphasizes the importance of protecting the skin from sun damage, offering products suitable for both morning and evening routines.
Morning routine
In the morning, it is crucial to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen such as BelleCôte's Double Sun Protection Cream. This cream combines the benefits of chemical and physical sunscreens, providing efficient UV protection.
Why do we call it Double Sun Protection cream?
This cream has Marine Sun filters (Chlorella and Spirulina), which increase sun protection up to 60 times? plus Sea Minerals that naturally reflect sunlight. Additionally, incorporating a moisturizer with SPF, like BelleCôte's Day Light moisturizer, ensures hydration and sun protection throughout the day.
Evening routine
In the evening, after a day of sun exposure, it is essential to cleanse the skin thoroughly to remove sunscreen, dirt, and impurities. Following cleansing, applying a nourishing moisturizer can help replenish and rejuvenate the skin while you sleep. BelleCôte Ultra Nourishing Night cream will be a perfect addition at this point of your routine.
Protecting our skin from the damaging effects of the sun is crucial for maintaining healthy and youthful-looking skin. By understanding how SPF works and incorporating quality sunscreen products like BelleCôte's Double Sun Protection Cream into our skincare routine, we can enjoy the sun safely while keeping our skin protected.
FAQ: Sunscreen Factors and Effectiveness
Q: How does the sunscreen factor work?
A: The sunscreen factor, commonly known as SPF (Sun Protection Factor), is a measure of a sunscreen's ability to protect your skin against harmful UV (ultraviolet) radiation from the sun. SPF primarily indicates the product's effectiveness in shielding the skin from UVB rays, which are responsible for causing sunburn. The higher the SPF number, the greater the protection against UVB rays.
Q: Which is better, SPF 30 or 50?
A: Both SPF 30 and SPF 50 offer effective sun protection, but the difference lies in their level of protection. SPF 30 filters out approximately 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 filters out around 98% of UVB rays. It's important to note that no sunscreen can provide 100% protection. Therefore, while SPF 50 offers slightly higher protection, the difference between SPF 30 and 50 is relatively small. The most crucial factor is proper and thorough application of sunscreen.
Q: How long will SPF 50 last?
A: The duration of SPF 50 protection depends on several factors, including individual skin type, sun exposure, and activities like swimming or sweating. As a general guideline, sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours or more frequently if you've been swimming, sweating, or toweling off. Despite its higher SPF, no sunscreen can provide all-day protection, so it's crucial to reapply regularly for continuous defense against harmful UV rays.


0 comments